
IOTA: History and About
IOTA is the creation of the German nonprofit organization, the IOTA Foundation, which came into existence in 2015 by David Sønstebø (business and technology expert), Dominik Schiener, Sergey Ivancheglo, and Dr. Serguei Popov (doctor of mathematics). These four remain the most crucial parts of IOTA’s core team, with every one of them being involved in the crypto community for a number of years prior.
IOTA also works in “partnership” (more on that later) with over 20 companies, which include Microsoft and Fujitsu, to launch a new data marketplace. This marketplace will be powered by distributed ledger technology, and the shareholders are encouraged to securely provide their data with IOTA tokens.
The IOTA Foundation also developed “The Big Deal” community funding project, which has the target of enticing and involving developers and corporations within the IOTA sphere. Participant individuals in The Big Deal get a share of IOTA tokens in return for their knowledge, developers, media publicity, and resources. Most of those involved in The Big Deal are not yet publicly known for legal reasons, but connections formed through The Big Deal can potentially increase both the value and practical use of IOTA.
How Does IOTA Work?
IOTA is the only crypto around which does not utilise blockchain technology. Instead, it uses another type of network, called a Tangle. According to IOTA’s website, the benefits of using Tangle include: a lack of fees, speedy transactions, secure data transfer and transactions can be conducted on infinite scales. Other aspects include pay-on-demand and micropayment abilities. IOTA was created to be “the backbone of the internet of things”, and fully supports secure machine-to-machine (m2m) communication.
First- and second-generation blockchains such as Bitcoin and Litecoin utilise transaction fees as a way to keep those using the network from spamming it. One transaction on the Bitcoin network costs around $0.50. This traditional model presents a potential issue for widespread, mainstream utilisation of Bitcoin as a substitute for fiat currency. The large volume of transactions that would be caused by many smaller Payments would, in turn, result in a large volume of fees.
IOTA finds a solution to this problem by being a zero-fee currency. The transaction fees on the Bitcoin network would discourage users from using Bitcoin for smaller purchases on an everyday scale. IOTA has no transaction fees and is therefore much better-suited to both practical and m2m (machine-to-machine) use.
IOTA as an Investment
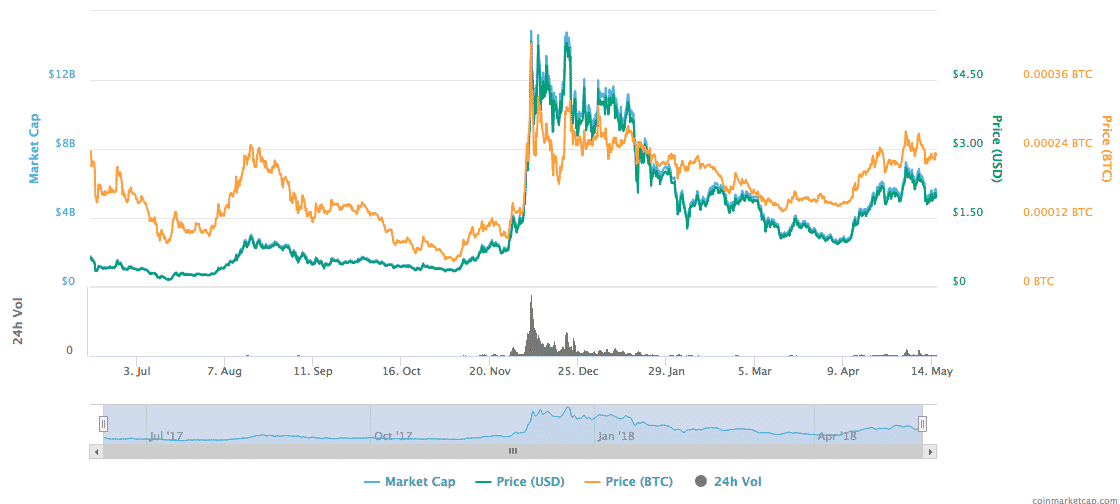
IOTA’s value has fluctuated over time just like many Cryptocurrencies around. Its peak market cap was in December of 2017, where it was valued at over $14 billion. However, since then it has come down to just over $5 billion at the turn of the year. It has been growing steadily since April, having reached a low of around $2.5 billion.
IOTA is currently traded on several major exchanges with the company planning on adding more in the future. Binance, Bitfinex, Coinone, OKEx, and Exrates are the ones that carry the coin at this moment.
MAny believe that IOTA’s technical value is not truly reflected in the current monetary valuation as it is still a concept that is to be fully realised. There are aspects of it which can be improved in the future as the Internet of Things fulfills its potential. Therefore, there is a lot of potential for the network to go further.
IOTA has a native wallet, the IOTA GUI Client. This wallet can be installed on a user’s desktop or as a mobile app. There is also an option for a paper wallet, which adds an extra layer of security.
Scandals and Controversy
On the whole, IOTA has not endured much in the way of scandals. However, there are still some aspects to consider and highlight in terms of controversy.
In January of this year, the wallets of some users were emptied by individuals operating malicious online seed generators. There were also Github wallets that were hacked, but this is (unfortunately) a fairly common incident in the cryptosphere.
Another aspect that’s already been mentioned is IOTA’s controversial relationship with Microsoft. It was initially suggested that the companies were in a partnership but it later emerged that the two had no formal working relationship, and that Microsoft was merely a participant in this case. It is unclear whether this was just misunderstanding by the media or deliberate misleading by IOTA.
There have also been some accusations of bullying and intimidation by certain factions of their team according to a Financial Times article, which claimed that IOTA does not take kindly to criticism. This can even be seen by their failed relationship with TheNextWeb, which was highlighted by IOTA’s official tweet:
https://twitter.com/iotatoken/status/966309603389698048
IOTA: History and About
IOTA is the creation of the German nonprofit organization, the IOTA Foundation, which came into existence in 2015 by David Sønstebø (business and technology expert), Dominik Schiener, Sergey Ivancheglo, and Dr. Serguei Popov (doctor of mathematics). These four remain the most crucial parts of IOTA’s core team, with every one of them being involved in the crypto community for a number of years prior.
IOTA also works in “partnership” (more on that later) with over 20 companies, which include Microsoft and Fujitsu, to launch a new data marketplace. This marketplace will be powered by distributed ledger technology, and the shareholders are encouraged to securely provide their data with IOTA tokens.
The IOTA Foundation also developed “The Big Deal” community funding project, which has the target of enticing and involving developers and corporations within the IOTA sphere. Participant individuals in The Big Deal get a share of IOTA tokens in return for their knowledge, developers, media publicity, and resources. Most of those involved in The Big Deal are not yet publicly known for legal reasons, but connections formed through The Big Deal can potentially increase both the value and practical use of IOTA.
How Does IOTA Work?
IOTA is the only crypto around which does not utilise blockchain technology. Instead, it uses another type of network, called a Tangle. According to IOTA’s website, the benefits of using Tangle include: a lack of fees, speedy transactions, secure data transfer and transactions can be conducted on infinite scales. Other aspects include pay-on-demand and micropayment abilities. IOTA was created to be “the backbone of the internet of things”, and fully supports secure machine-to-machine (m2m) communication.
First- and second-generation blockchains such as Bitcoin and Litecoin utilise transaction fees as a way to keep those using the network from spamming it. One transaction on the Bitcoin network costs around $0.50. This traditional model presents a potential issue for widespread, mainstream utilisation of Bitcoin as a substitute for fiat currency. The large volume of transactions that would be caused by many smaller Payments would, in turn, result in a large volume of fees.
IOTA finds a solution to this problem by being a zero-fee currency. The transaction fees on the Bitcoin network would discourage users from using Bitcoin for smaller purchases on an everyday scale. IOTA has no transaction fees and is therefore much better-suited to both practical and m2m (machine-to-machine) use.
IOTA as an Investment
IOTA’s value has fluctuated over time just like many Cryptocurrencies around. Its peak market cap was in December of 2017, where it was valued at over $14 billion. However, since then it has come down to just over $5 billion at the turn of the year. It has been growing steadily since April, having reached a low of around $2.5 billion.
IOTA is currently traded on several major exchanges with the company planning on adding more in the future. Binance, Bitfinex, Coinone, OKEx, and Exrates are the ones that carry the coin at this moment.
MAny believe that IOTA’s technical value is not truly reflected in the current monetary valuation as it is still a concept that is to be fully realised. There are aspects of it which can be improved in the future as the Internet of Things fulfills its potential. Therefore, there is a lot of potential for the network to go further.
IOTA has a native wallet, the IOTA GUI Client. This wallet can be installed on a user’s desktop or as a mobile app. There is also an option for a paper wallet, which adds an extra layer of security.
Scandals and Controversy
On the whole, IOTA has not endured much in the way of scandals. However, there are still some aspects to consider and highlight in terms of controversy.
In January of this year, the wallets of some users were emptied by individuals operating malicious online seed generators. There were also Github wallets that were hacked, but this is (unfortunately) a fairly common incident in the cryptosphere.
Another aspect that’s already been mentioned is IOTA’s controversial relationship with Microsoft. It was initially suggested that the companies were in a partnership but it later emerged that the two had no formal working relationship, and that Microsoft was merely a participant in this case. It is unclear whether this was just misunderstanding by the media or deliberate misleading by IOTA.
There have also been some accusations of bullying and intimidation by certain factions of their team according to a Financial Times article, which claimed that IOTA does not take kindly to criticism. This can even be seen by their failed relationship with TheNextWeb, which was highlighted by IOTA’s official tweet:
https://twitter.com/iotatoken/status/966309603389698048
This news is republished from another source. You can check the original article here



